Helpful Guides on each Category
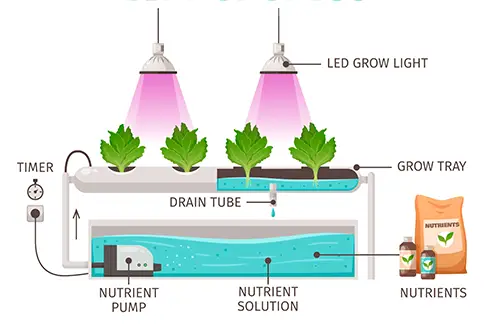
Hydroponic system involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, without soil. That means you will grow plants indoors, any time of year, without worrying about the weather or pests.
Are you keen on growing plants but lack outdoor space or good soil? Fear not, my friend! The hydroponic gardening system covers that.
In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll walk you through the basics of hydroponic planting, from the different types of systems available to the necessary equipment and the best plants to grow.
As an experienced farmer or beginner, this guide is the perfect way to get started with hydroponic planting and enjoy the benefits of fresh, home produce.
Read Also 39+ Best Hydroponic plants (Vegetables, Greens, Herbs and fruits) to grow Indoors hydroponically
What is a Hydroponic System?

A hydroponic system is a way of growing plants without soil. Plants grow in a nutrient-rich solution that is directly fed to the roots.
Hydroponic systems come in many different shapes and sizes, but they all have the same basic components: a reservoir for the nutrient solution, a pump to circulate the solution, and a way to deliver the solution to the roots of the plants.
One of the great advantages of hydroponics is that it allows for precise control of the plant’s environment, such as pH levels and nutrient concentrations. This results in faster growth rates and higher yields compared to traditional soil-based growing methods.
Areas with poor soil quality or limited space make use of the hydroponic system of planting. This makes it a popular choice for urban and indoor farming.
A variety of plants, including vegetables, herbs, and even flowers are grown this way.
They are either simple and small for home use, or large and complex for commercial farming.
So if you’re interested in growing your plants but don’t have access to quality soil or space, a hydroponic system is the perfect solution for you!
Read on 15+ Best Perennials For Shade. Easy-To-Grow For Shady Gardens.
Types of Hydroponic Systems
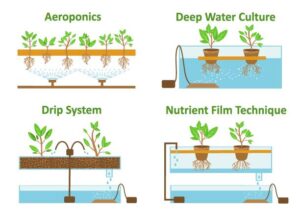
There are several types of hydroponic systems, each with its unique features and benefits.
Here are some of the most common types:
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
In this system, plants are suspended in a nutrient-rich solution and their roots are constantly submerged in the water. This type of system is great for beginners because it’s simple and easy to set up. Beginners prefer using this method.
Drip Irrigation
This system involves using a pump to drip nutrient solution onto the plant’s roots. Excess solution is collected and recirculated back to the reservoir. Drip irrigation is a popular choice for larger-scale hydroponic setups.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
In NFT systems, a thin film of nutrient solution is continuously flowing over the roots of the plants, providing them with a constant supply of nutrients. This system is great for plants that prefer a well-oxygenated root zone.
Aeroponics
In this system, plants are suspended in the air and their roots are misted with a nutrient solution. This creates a highly oxygenated environment for the roots and results in very fast growth rates.
Ebb and Flow
This system involves flooding the plants’ roots with nutrient solution and then draining it back into the reservoir. This cycle repeats regularly, providing the plants with a periodic supply of nutrients.
Wick System
This is the simplest and most low-tech type of hydroponic system. It involves placing a wick in a nutrient solution and using it to draw the solution up to the plant’s roots. This is the best for smaller plants with low nutrient requirements.
Vertical Hydroponic System
This type of system is designed to maximize growing space by growing plants vertically, often in towers or columns. Plants are grown in a soilless medium and fed with a nutrient solution. Vertical hydroponic systems are ideal for urban or indoor gardening where space is limited.
As with any hydroponic system, the type you choose will depend on your individual needs and preferences. Each system has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to do your research and select the one that’s right for you.
With a little bit of effort and experimentation, you will enjoy the benefits of growing plants hydroponically and enjoy fresh, healthy produce all year round!
Advantages of Hydroponic System over Traditional Soil Planting

Hydroponic systems offer several advantages over traditional soil planting, including:
- Water Conservation: Hydroponic systems use significantly less water than traditional soil planting. This is because the nutrient solution is recirculated and reused, whereas soil-based plants require more water to maintain proper hydration levels.
- Faster Growth Rates: Plants receive a constant supply of nutrients and oxygen, which results in faster growth rates and higher yields compared to traditional soil planting.
- Space Efficiency: Hydroponic systems are much more space-efficient than traditional soil planting. This makes them ideal for indoor gardening, where space is often limited.
- Precise Control: Hydroponic systems allow for precise control of the growing environment, including nutrient levels, pH balance, and lighting.
- No Soil-Borne Diseases: Since hydroponic systems don’t use soil, there’s no risk of soil-borne diseases or pests affecting your plants. This reduces the need for pesticides and other chemicals.
- Reduced Labor: Less labour than traditional soil planting, as there’s no need for tilling, weeding, or other maintenance tasks associated with soil-based farming.
- Year-Round Growing: Set up indoors, allows for year-round growing regardless of weather conditions. This is particularly useful in areas with cold winters or hot summers, where traditional outdoor planting is not possible.
- Higher Crop Yields: Because hydroponic systems provide plants with a constant supply of nutrients, oxygen, and water, they produce higher crop yields than traditional soil planting. This is very true for crops like lettuce, herbs, and strawberries.
For you How To Effectively Get Rid Of Rats In Your Garden
Equipment and materials needed to Build a hydroponic garden
Here is a list of the equipment and materials needed to build a hydroponic garden, categorized by function or use:
Structural Components:
- Grow Tent or Space: To contain the hydroponic system and regulate the growing environment.
- Grow Light: To provide artificial light for plants to grow.
- Reflective Material: To reflect light and increase efficiency.
- Ducting: To connect the grow light to the exhaust fan and allow for air circulation.
- Exhaust Fan: To control the temperature and humidity inside the grow space.
Hydroponic System Components:
- Reservoir: To hold the nutrient solution.
- Net Pots: To hold the plants and allow their roots to access the nutrient solution.
- Growing Medium: To support the plants and provide a surface for the roots to grow on.
- Submersible Pump: To circulate the nutrient solution and supply it to the plants.
- Air Pump: To oxygenate the nutrient solution and prevent root rot.
- Air Stones: To diffuse the oxygen from the air pump into the nutrient solution.
Nutrient Components:
- Hydroponic Nutrient Solution: To provide the necessary nutrients for plant growth.
- pH Test Kit: To monitor and adjust the pH level of the nutrient solution.
- EC Meter: To monitor and adjust the electrical conductivity (EC) of the nutrient solution.
Extra Optional Accessories:
- Timer: To automate the pump and light cycles.
- Temperature and Humidity Monitor: To track the growing environment.
- CO2 Generator: To increase CO2 levels and enhance plant growth.
- Water Chiller: To maintain optimal water temperature in the reservoir.
Check too 21 Common Toxic Houseplants To Avoid Around Pets And Children
Step-by-step Guide on how to assemble a hydroponic system at home

There are many ways to structure and style the build of your hydroponic planting system. Space, hydroponic method, the capacity of the farm, and design choice are factors that help you decide what your farm will look like.
Whatever way we discuss below is what we consider very easy and effective for a beginner to set up. You should be more creative than I am.
Step 1: Choose a suitable location
Choose a location that is convenient and provides access to a power outlet. Make sure the location has enough space to accommodate the hydroponic system and allows for proper ventilation.
Step 2: Gather Materials
Gather all the necessary materials and equipment for your hydroponic system. This includes a reservoir, net pots, growing medium, submersible pump, air pump, air stones, hydroponic nutrient solution, pH test kit, and EC meter.
Step 3: Set Up the Reservoir
Fill the reservoir with water and add the appropriate amount of hydroponic nutrient solution, according to the instructions on the package. Use the pH test kit to adjust the pH level of the nutrient solution to the optimal range for your plants.
Step 4: Install Submersible Pump
Install the submersible pump in the reservoir, making sure it is securely anchored to the bottom.
Step 5: Set Up Air Pump
Connect the air pump to the air stones and place them in the reservoir. This will help oxygenate the nutrient solution and prevent root rot.
Step 6: Prepare Net Pots
Fill the net pots with the chosen growing medium, such as rock wool or hydroton, and insert the plants.
Step 7: Place Net Pots in Hydroponic System
Place the net pots in the hydroponic system, making sure the roots are submerged in the nutrient solution.
Step 8: Turn on the System
Turn on the submersible pump and air pump, and adjust the timer settings if you are using one.
Step 9: Monitor and Adjust
Monitor the pH level and EC of the nutrient solution regularly and adjust if necessary. Monitor the temperature and humidity of the grow space to ensure optimal growing conditions for your plants.
Step 10: Harvest and Enjoy
Once the plants have grown to maturity, harvest them and enjoy fresh, healthy produce!
Building a hydroponic system at home requires a bit of planning and preparation, but with the right materials and equipment, it is done easily and efficiently.
Choosing Plants for Hydroponic System Planting

Here are some tips to help you choose the right plants for your hydroponic garden:
- Choose plants that grow well in hydroponic systems: Some plants are better suited to hydroponic systems than others. Look for plants that have a relatively short growing cycle and thrive in a nutrient-rich, water-based environment.
- Consider space requirements: Depending on the size of your hydroponic system, you may need to choose plants that have a smaller footprint. Choose plants that grow vertically or can be pruned and trained to take up less space.
- Choose disease-resistant plants: Because hydroponic systems are essentially soilless, they are less likely to be affected by soil-borne diseases. However, it’s still important to choose plants that are disease-resistant to prevent any potential problems.
- Think about light requirements: Different plants have different light requirements, so choose plants that are well-suited to the amount and type of light you will provide. You may need to invest in grow lights to ensure optimal growth for certain types of plants.
- Consider nutritional needs: Make sure the plants you choose have the appropriate nutritional needs for hydroponic growing. Look for plants that have a relatively low nitrogen requirement and are high in potassium and phosphorus.
- Choose plants that you enjoy eating: Finally, choose plants that you enjoy eating! One of the great benefits of hydroponic gardening is the ability to grow fresh, delicious produce right at home, so make sure you’re choosing plants that you’ll actually want to eat.
Types of plants best suited for hydroponic System plantings
There are many plants that are well-suited to hydroponic plantings. Leafy greens, hydroponic strawberries, and tomatoes are suitable plants for a hydroponic farm.
Here are some of the most popular types of plants for hydroponic gardening:
- Leafy greens: Plants like lettuce, spinach, kale, and arugula are all great choices for hydroponic systems. They have relatively short growing cycles and are harvested multiple times, making them a popular choice for home gardeners.
- Herbs: Many herbs are well-suited to hydroponic gardening, including basil, cilantro, parsley, and mint. They are grown in small spaces and require relatively little maintenance, making them a great choice for beginners.
- Tomatoes: Tomatoes are a popular choice for hydroponic gardening because they are grown vertically and have a short growing cycle. They do require a bit more attention than some other plants, but the reward is fresh, delicious tomatoes all year round.
- Peppers: Peppers are another popular choice for hydroponic gardening. They require a bit more space than some other plants, but they are relatively easy to grow and produce a bountiful harvest of spicy peppers.
- Strawberries: Strawberries in hydroponic systems are a great choice for anyone looking for a sweet treat. They require a bit more attention than some other plants, but the reward is fresh, juicy strawberries all year round.
These are just a few of the many plants that are well-suited to hydroponic gardening.
Types of Hydroponic System Nutrient Solutions
There are two main types of hydroponic nutrient solutions: pre-mixed solutions and DIY solutions.
- Pre-mixed nutrient solutions: Pre-mixed nutrient solutions come in a variety of formulations designed for different stages of plant growth. They contain a balanced mix of essential nutrients and are easy to use, making them a popular choice for many hydroponic gardeners. Some popular brands of pre-mixed nutrient solutions include General Hydroponics, Fox Farm, and Advanced Nutrients.
- DIY nutrient solutions: DIY nutrient solutions allow hydroponic gardeners to customize the nutrient mix to suit the specific needs of their plants. These solutions are made from scratch using individual nutrient salts, or by combining pre-mixed base nutrients with additional supplements. DIY nutrient solutions require more knowledge and effort to create, but they offer greater flexibility and control over the nutrient mix.
It’s important to choose a nutrient solution that is appropriate for the type of plants you are growing, as well as their stage of growth.
Some nutrient solutions are designed specifically for certain types of plants, such as tomatoes or cannabis, while others are formulated for use during different stages of growth, such as vegetative or flowering.
How to choose the right nutrient solution for each type of plant
Here are some tips to help you choose the right nutrient solution for your plants:
Know your plant’s nutritional requirements
Different plants have different nutritional requirements, so it’s important to understand what your plants need. Look up the specific nutrient requirements for the plants you plan to grow and choose a nutrient solution that meets those requirements.
Choose a balanced nutrient solution
A balanced nutrient solution should contain the major macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) as well as essential micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and iron. Look for a nutrient solution that provides a balance of these nutrients to ensure healthy plant growth.
Consider pH levels
The pH level of your nutrient solution is important for ensuring optimal nutrient uptake by your plants. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic pH level between 5.5 and 6.5. Make sure your nutrient solution is within this range, and adjust it as necessary using pH adjusters.
Choose between organic or synthetic nutrients
Organic solutions are derived from natural sources and are typically more expensive, but they may be more beneficial for certain types of plants. Synthetic solutions are made from chemical compounds and are typically less expensive, but may not be as sustainable as organic options.
Choose a reputable brand
When choosing a nutrient solution for your hydroponic garden, it’s important to choose a reputable brand that has a proven track record of success. Look for brands that specialize in hydroponic gardening and have a strong reputation within the industry.
how to adjust the pH level of Hydroponic nutrient solution
Adjusting the pH level of hydroponic nutrient solution is essential for healthy plant growth. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic pH level between 5.5 and 6.5. Here’s how to adjust the pH level of your nutrient solution:
- Measure the pH level: Use a pH meter or test strips to measure the current pH level of your nutrient solution.
- Determine how much to adjust: If the pH level is too high (above 6.5), you’ll need to lower it with an acidic solution. If the pH level is too low (below 5.5), you’ll need to raise it with an alkaline solution. The amount you’ll need to adjust the pH level depends on how far off it is from the ideal range.
- Add the adjustment solution: Slowly add the pH adjustment solution to your nutrient solution while stirring continuously. Follow the instructions on the product label for the recommended amount to add.
- Measure the pH level again: After adding the adjustment solution, measure the pH level again to ensure it’s within the ideal range. If it’s still too high or too low, repeat the process until you reach the desired pH level.
It’s important to adjust the pH level of your nutrient solution regularly, as it changes over time due to factors such as plant uptake and evaporation.
Maintaining a Hydroponic Garden

Maintaining a hydroponic garden seem like a burden at first, but it’s actually easy once you get the hang of it.
Here are some tips on how to maintain your hydroponic garden:
1. Check pH and nutrient levels regularly
pH and nutrient levels are crucial to plant health, so it’s important to monitor them regularly using a pH test kit and EC meter. Adjust the levels as needed to ensure your plants are getting the right nutrients and pH balance.
2. Inspect plants for signs of pests and disease
Keep an eye out for any signs of pests or disease on your plants, such as yellowing leaves, spots, or wilting. If you notice any problems, take action quickly to prevent further damage.
3. Monitor water and nutrient levels
Check the water and nutrient levels in your reservoir regularly and top up as needed. Be sure to change out the nutrient solution completely every 1-2 weeks to prevent the buildup of salts and other minerals.
4. Clean and maintain equipment
Keep your equipment clean and well-maintained to prevent problems and ensure optimal performance. Clean the reservoir, pumps, and air stones regularly to prevent clogs and bacteria buildup.
5. Control temperature and humidity
Maintain the proper temperature and humidity levels in your grow space to prevent problems like mould and mildew. Use a thermometer and hygrometer to monitor levels and adjust as needed.
6. Prune and train plants
Keep your plants pruned and trained to prevent overcrowding and promote optimal growth. Remove any dead or damaged leaves or branches, and use trellises or supports to keep plants upright.
7. Harvest regularly
Harvest your plants regularly to promote new growth and prevent overcrowding. Be sure to clean and sanitize your tools between each harvest to prevent the spread of disease.
Nutrient Requirements for Hydroponic Plants
Hydroponic plants require a specific balance of nutrients to thrive. Unlike traditional soil planting, hydroponic plants receive all of their nutrients from the nutrient solution, so it’s important to ensure that the solution contains the right balance of macronutrients and micronutrients.
Here are the main nutrients that hydroponic plants require which must be in your nutrient solution:
- Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen is essential for vegetative growth and the production of chlorophyll. Plants use nitrogen to build proteins, enzymes, and other essential compounds.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus is necessary for root development, energy storage, and the production of flowers and fruits. It also helps plants absorb and use other nutrients.
- Potassium (K): Potassium is important for plant growth and development, including the formation of strong stems and the regulation of water balance within the plant.
- Calcium (Ca): Calcium is essential for the formation of strong cell walls, and helps prevent diseases like blossom end rot.
- Magnesium (Mg): Magnesium is necessary for the production of chlorophyll and other essential plant compounds.
- Sulfur (S): Sulfur is important for protein synthesis and helps plants withstand stress.
- Iron (Fe): Iron is necessary for the formation of chlorophyll and the transport of oxygen within the plant.
- Manganese (Mn): Manganese is important for photosynthesis and helps plants withstand stress.
- Zinc (Zn): Zinc is necessary for the formation of enzymes and helps plants grow and develop.
- Copper (Cu): Copper is essential for plant growth and helps with the formation of enzymes.
Importance of Monitoring Nutrient Levels in a Hydroponic System

Monitoring nutrient levels in a hydroponic system is crucial for the health and success of your plants.
Here are some reasons why:
- Avoid overfeeding or underfeeding: If nutrient levels are too high, it causes nutrient burn, which damage or kills your plants. Also, if nutrient levels are too low, your plants may not receive the necessary nutrients for healthy growth. Regular monitoring helps you adjust nutrient levels as needed to avoid these problems.
- Identify nutrient deficiencies: Certain nutrient deficiencies cause symptoms in plants, such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth. By monitoring nutrient levels, you will identify and address these deficiencies before they become severe and affect plant health.
- Optimize plant growth: Different plants have different nutrient requirements at different stages of growth. Monitoring nutrient levels allows you to adjust the nutrient mix to suit the specific needs of your plants, which promotes optimal growth and yield.
- Prevent system imbalances: Hydroponic systems rely on a delicate balance of nutrients, pH, and other factors. Regular monitoring helps you identify and address imbalances in the system before they cause problems for your plants.
Common Challenges in Hydroponic Planting and How to Overcome Them
Hydroponic planting is a method of growing plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water instead. While hydroponic planting has many benefits, such as faster growth rates and increased yields, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Here are some of the most common challenges in hydroponic planting and how to overcome them:
1. Algae Growth
Algae growth occurs in hydroponic systems due to excess light or nutrients in the water. This causes blockages in the system and competes with plants for nutrients.
Solution:
Control the amount of light and nutrients in the water. Use an opaque material to cover the nutrient solution and clean the system regularly.
2. pH Imbalances
pH imbalances affect nutrient uptake by plants, resulting in stunted growth or death.
Solution:
Test the pH level of the nutrient solution regularly and adjust it accordingly using pH up or down solutions.
3. Nutrient Deficiencies
Hydroponic plants are entirely dependent on the nutrient solution for their growth, and nutrient deficiencies cause various problems such as leaf yellowing, stunted growth, and poor yields.
Solution:
Monitor nutrient levels regularly, adjust the nutrient solution accordingly, and use high-quality nutrient solutions to prevent deficiencies.
4. Waterborne Diseases
Waterborne diseases, such as Pythium and Fusarium spread rapidly in hydroponic systems, leading to plant death.
Solution:
Ensure the system is clean and disinfected regularly, use sterile growing media, and avoid overwatering.
5. Temperature Fluctuations
Extreme temperatures affect plant growth and lead to plant death.
Solution:
Use a temperature-controlled environment and adjust the temperature to suit the specific plant species.
6. Pest Infestations
Pests such as spider mites, thrips, and aphids can infest hydroponic systems and cause significant damage to plants.
Solution:
Regularly inspect the plants for signs of infestation and use appropriate pest control measures, such as insecticidal soaps or neem oil.
7. Lack of Oxygen
Another common challenge in hydroponic planting is a lack of oxygen in the nutrient solution. This occurs when the water becomes stagnant, preventing the roots from receiving the necessary oxygen to grow and function properly.
Solution:
Ensure that the nutrient solution is well-aerated by using air stones, diffusers, or other oxygenating equipment. Also, avoid overwatering and ensure that the water is circulating adequately through the system.
Don’t you want fresh farm produce all season?
Hydroponic system of planting is an exciting and innovative way to grow plants without soil. It offers numerous benefits, such as higher yields, faster growth rates, and the ability to grow crops year-round.
By following the steps outlined in this beginner’s guide, you will start your hydroponic garden with ease and enjoy the benefits of fresh, home-grown produce.
Remember to choose the right system for your needs, maintain proper nutrient and pH levels, ensure adequate oxygenation, and keep your system clean and free of pests and diseases. With a little patience and dedication, you can successfully grow a variety of plants using hydroponic methods.
Whether you’re looking to start a small herb garden or a large-scale commercial operation, hydroponic planting offers a versatile and efficient solution for your needs.
So why not give it a try and see the benefits for yourself? Happy planting!
Types of Hydroponic Gardening system
There are several different types of hydroponic systems, each with its own advantages and best-suited plants. Here are some of the most common hydroponic systems and the plants that grow best in them:
- Deep Water Culture (DWC) – In a DWC system, plants grow in a nutrient-rich water solution that is constantly aerated. This system is best for plants that thrive in wet environments, such as lettuce, spinach, and herbs.
- Drip System – In a drip system, a pump delivers a nutrient solution to the plants through a series of tubes or pipes. This system is great for larger plants that need more water, such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) – In an NFT system, a thin film of nutrient-rich water flows over the roots of the plants. This system is best for small, fast-growing plants like lettuce, spinach, and herbs.
- Aeroponics – Here, plants are suspended in the air and the roots are misted with a nutrient solution. This system is ideal for plants that require high levels of oxygen, such as lettuce, spinach, and herbs.
- Ebb and Flow – Plants sit in a tray or container that is periodically flooded with a nutrient solution. This system is great for a variety of plants, including tomatoes, peppers, and herbs



